In the pursuit of academic success, mastering memory is a crucial key to unlocking the door to effective learning. In this article, we explore proven strategies grounded in scientific research to enhance memory retention. Whether you're a student preparing for exams or a lifelong learner, these techniques provide a roadmap for mastering memory and optimising your study recall!
#1 Use spaced-repetition
German psychologist Hermann Ebbinghaus introduced the concept of the forgetting curve in the late 19th century. The forgetting curve is a graphical representation of how information is forgotten over time if it is not reinforced through repetition or other memory-strengthening techniques.
Ebbinghaus conducted experiments on himself, memorising lists of nonsense syllables and then measuring how much he could remember at various intervals. He found that forgetting happens most rapidly in the initial hours and days after learning something new, and the rate of forgetting tends to decrease over time. The curve typically shows a steep decline in memory retention shortly after learning, followed by a more gradual decline.
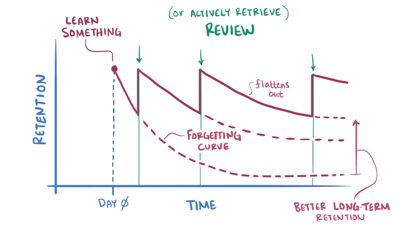
But most importantly, Ebbinghaus introduced the concept of spaced-repetition which suggests that spacing out repetitions of information over time is more effective for long-term retention than cramming or massed practice.
#2 Improve understanding using the Feynman Technique
The Feynman Technique is a learning and study method designed to help learners understand complex concepts and remember information more effectively. The technique involves four key steps:
Step 1: Choose a Concept. Select the concept or topic you want to learn and understand. This could be a new idea, a theory, a problem, or any other subject matter.
Step 2: Try to explain it to a 5-year-old. Use plain language and simple examples to explain the concept. If you find it difficult to explain a particular point, it indicates an area where you need to focus your further study.
Step 3: Identify gaps in your knowledge. As you explain the concept, pay attention to any areas where your understanding falters or where you struggle to express the ideas clearly. Then, go back to your study materials to review and refine your understanding of those specific points.
Step 4: Repeat and simplify. Teach the concept again, but this time focus on simplifying your explanation even further. The goal is to achieve a level of understanding where you can explain the concept in the simplest terms possible.
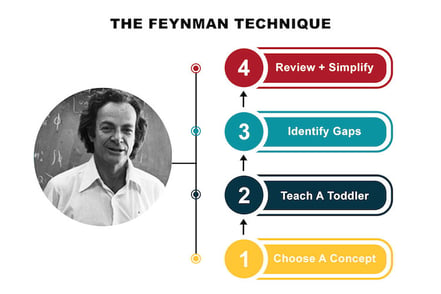
Why is the Feynman Technique so effective? First, it encourages active learning and engagement with the material. Second, it highlights the importance of being able to communicate complex ideas in simple terms, which often reveals the depth of one's understanding. Lastly, the iterative nature of the technique—going back to review and refine understanding—reinforces the learning process.
#3 Exercise right before learning
Have you ever noticed that right after exercising, you often feel more alert and focused? One of the reasons is something called BDNF (Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor). This neurotrophic factor acts as a sort of brain fertiliser, promoting the growth and connectivity of neurons. As a result, not only does exercise benefit your physical health, but it also creates an optimal environment for your brain to function at its best, improving your ability to concentrate, learn, and retain information.
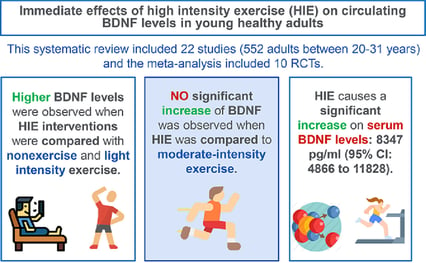 "Immediate effect of high-intensity exercise on brain-derived
"Immediate effect of high-intensity exercise on brain-derived
neurotrophic factor in healthy young adults"
#4 Manage your time using the Pomodoro Technique
The Pomodoro Technique is a time management method developed by Francesco Cirillo in the late 1980s. It's a simple and effective technique that helps improve focus and productivity. Here's how it works:
Step 1: Choose a Task. Select a task that you want to work on.
Step 2: Set a Timer. Set a timer for 25 minutes (this interval is known as one "Pomodoro"). During this time, focus exclusively on the chosen task.
Step 3: Work on the Task. Work on it with full concentration until the timer rings.
Step 4: Take a Short Break. When the timer goes off, take a 5-minute break to relax, stretch, or do something enjoyable.
Step 5: Repeat. After the short break, go back to the task and start another Pomodoro (25-minute work session). Repeat this process.
Step 6: Long Break. After completing four Pomodoros, take a longer break of around 30 minutes.

The key idea is to break your work into focused, manageable intervals with short breaks in between. This helps prevent burnout, maintain concentration, and enhance overall productivity.
#5 Double the speed of your class videos and watch them twice
With more and more lectures being recorded and watched by students from home, it's interesting to know more about how the way recordings are consumed can affect learning outcomes and knowledge retention.
After discovering that 85% of UCLA college students usually watched pre-recorded lectures at faster than normal speed, researchers explored the impact that sped-up viewing has on learning in a recent UCLA study. The result? If used strategically, it can actually improve learning!
First, the study shows that students who watched lecture videos at 2x speed retained just as much information over the course of a week as those who watched at normal speed.
But more importantly, researchers found that students who watched the same 2x video again immediately prior to taking a test earned higher scores than those who only watched the video once!
So to sum this up: you can save time and learn more efficiently by watching pre-recorded lectures at 2x speed twice (including once just before taking a test)!
%20Graph%20of%20Testing%20Effect.png?width=339&height=231&name=Roediger%20%26%20Karpicke%20(2006)%20Graph%20of%20Testing%20Effect.png) The study involved college students who were asked to learn a series of short passages. They were divided into two groups: one group engaged in repeated studying, where they read the passages multiple times, and the other group practiced retrieval by taking recall tests on the passages. They were then tested on their memory of the passages either immediately after the study/test phase or after a delay of one week.
The study involved college students who were asked to learn a series of short passages. They were divided into two groups: one group engaged in repeated studying, where they read the passages multiple times, and the other group practiced retrieval by taking recall tests on the passages. They were then tested on their memory of the passages either immediately after the study/test phase or after a delay of one week.
 by:Jeanne Aimerie on: December 1, 2023
by:Jeanne Aimerie on: December 1, 2023





-2.png)
